Atmosphere but some of the outgoing long wavelength energy is absorbed and
Home » Query » Atmosphere but some of the outgoing long wavelength energy is absorbed andYour Atmosphere but some of the outgoing long wavelength energy is absorbed and images are available in this site. Atmosphere but some of the outgoing long wavelength energy is absorbed and are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Atmosphere but some of the outgoing long wavelength energy is absorbed and files here. Find and Download all royalty-free photos.
If you’re looking for atmosphere but some of the outgoing long wavelength energy is absorbed and pictures information linked to the atmosphere but some of the outgoing long wavelength energy is absorbed and interest, you have visit the right blog. Our site always provides you with suggestions for viewing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly surf and find more informative video articles and images that fit your interests.
Atmosphere But Some Of The Outgoing Long Wavelength Energy Is Absorbed And. The dips in the incoming and outgoing energy are where the atmosphere absorbs energy. However since the Earth is much cooler than the Sun its radiating energy is much weaker long wavelength infrared energy. Incoming energy from the sun and outgoing energy from the earth relative to the electromagnetic spectrum. Some of this radiated energy will dissipate into space but a significant amount of heat will be absorbed by the atmosphere.
 The Absorption Band Graphs Of Gh Gases In The Atmosphere In The Aga Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
The Absorption Band Graphs Of Gh Gases In The Atmosphere In The Aga Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
Some of the incoming energy is absorbed by the atmosphere whereas most of the infrared energy emitted by the earth is absorbed. Some of this radiation is absorbed by the atmosphere directly but the majority is absorbed by the surface. When it reaches the Earth some is reflected back to space by clouds some is absorbed by the atmosphere and some is absorbed at the Earths surface. Some of that flux F g is absorbed by the atmosphere through its long wavelength transmittance T t where 0 t t 10. Some gases in the atmosphere can absorb Earths long-wave radiation and heat up the surrounding air by collisions with the neighboring molecules. This energy is ultimately reradiated back into the atmosphere from the surface at a.
However since the Earth is much cooler than the Sun its radiating energy is much weaker long wavelength infrared energy.
Incoming short- and intermediate-wavelength radiation may be absorbed by gases in the atmosphere reflected back into space from the atmosphere or Earths surface or absorbed by Earths surface. Incoming short- and intermediate-wavelength radiation may be absorbed by gases in the atmosphere reflected back into space from the atmosphere or Earths surface or absorbed by Earths surface. Some of the incoming energy is absorbed by the atmosphere whereas most of the infrared energy emitted by the earth is absorbed. The ground then re-radiates that heat as outgoing long wavelength IR radiation F g. Energy released from the Sun is emitted as shortwave light and ultraviolet energy. This outgoing long wave radiation emitted by the earth surface is called terrestrial radiation.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
A large portion of electromagnetic energy is scattered refracted diffused and reflected by the surface and atmosphere. One of the most important factors is the greenhouse effect a simplified explanation of which is as follows Short-wave solar radiation can pass through the clear atmosphere relatively unimpeded But long-wave terrestrial radiation emitted by the warm surface of the Earth is partially absorbed and then re-emitted by a number of trace gases in the cooler atmosphere above Since on average the outgoing. This is the basis for the greenhouse effect Figure 812. Incoming and outgoing long-wavelength radiation is absorbed by water vapor carbon dioxide and other gases in the atmosphere. As the water vapour methane carbon dioxide molecules absorb the longwave radiation they heat.
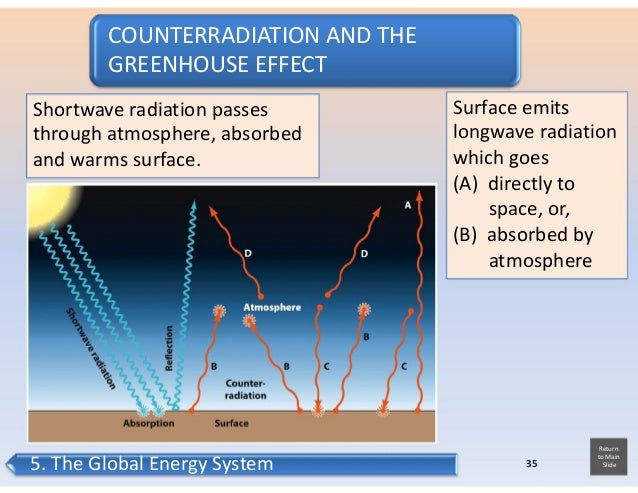 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
The ground then re-radiates that heat as outgoing long wavelength IR radiation F g. Incoming short- and intermediate-wavelength radiation may be absorbed by gases in the atmosphere reflected back into space from the atmosphere or Earths surface or absorbed by Earths surface. Some of the incoming energy is absorbed by the atmosphere whereas most of the infrared energy emitted by the earth is absorbed. The ground then re-radiates that heat as outgoing long wavelength IR radiation F g. That flux is absorbed by the ground and the ground heats up to some temperature T g.

Exchange of Terrestrial Radiation. Some of this radiation is absorbed by the atmosphere directly but the majority is absorbed by the surface. When it reaches the Earth some is reflected back to space by clouds some is absorbed by the atmosphere and some is absorbed at the Earth. The atmosphere contains certain components most notably water molecules that absorb some wavelengths of outgoing longwave radiation OLR. Greenhouse gases are molecules in the atmosphere that absorb long-wavelength infrared energy radiated by the Earth.
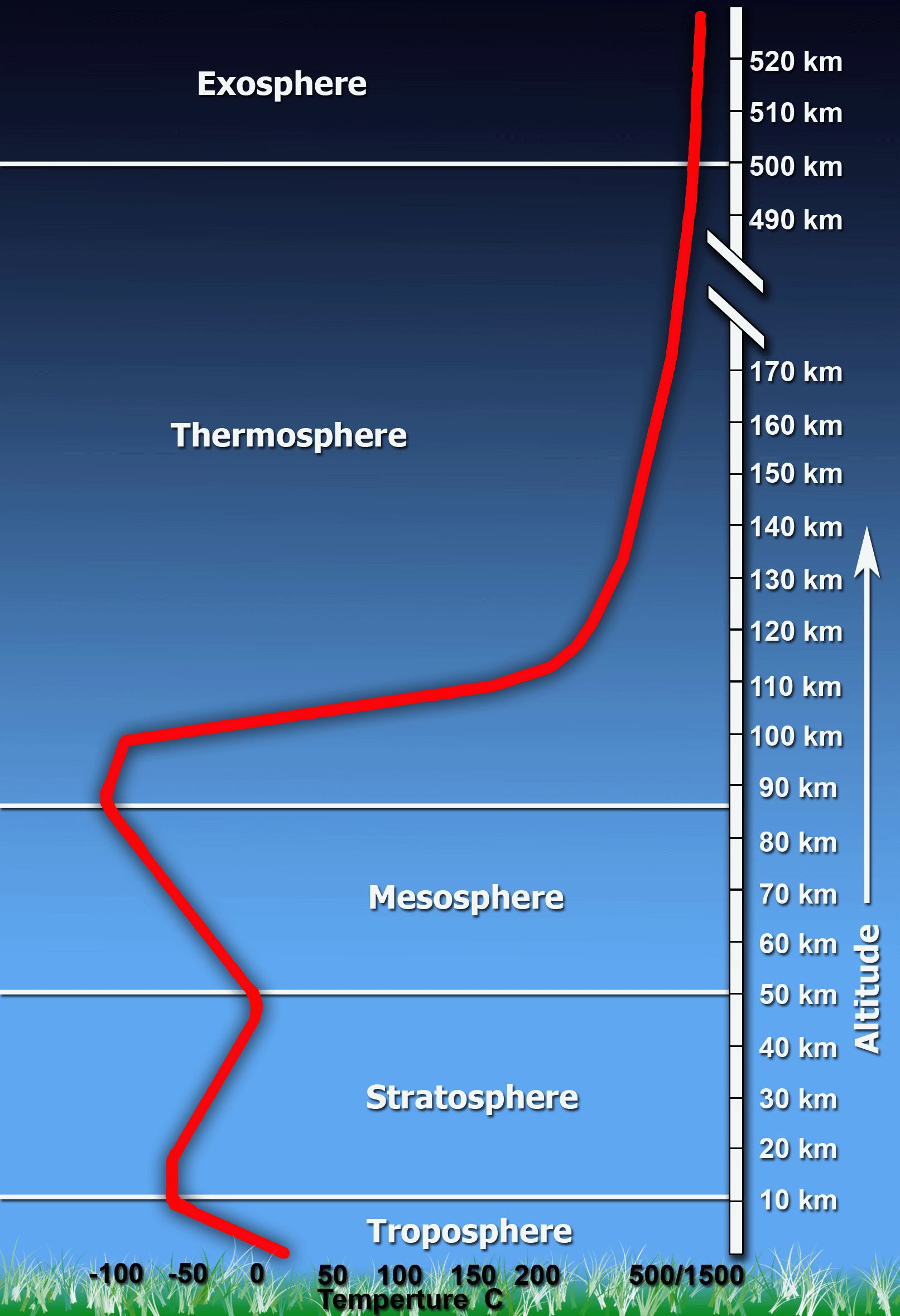 Source: ces.fau.edu
Source: ces.fau.edu
Frequency is related to wavelength by λ. Incoming and outgoing long-wavelength radiation is absorbed by water vapor carbon dioxide and other gases in the atmosphere. Some of that flux F g is absorbed by the atmosphere through its long wavelength transmittance T t where 0 t t 10. The ground then re-radiates that heat as outgoing long wavelength IR radiation F g. Exchange of Terrestrial Radiation.
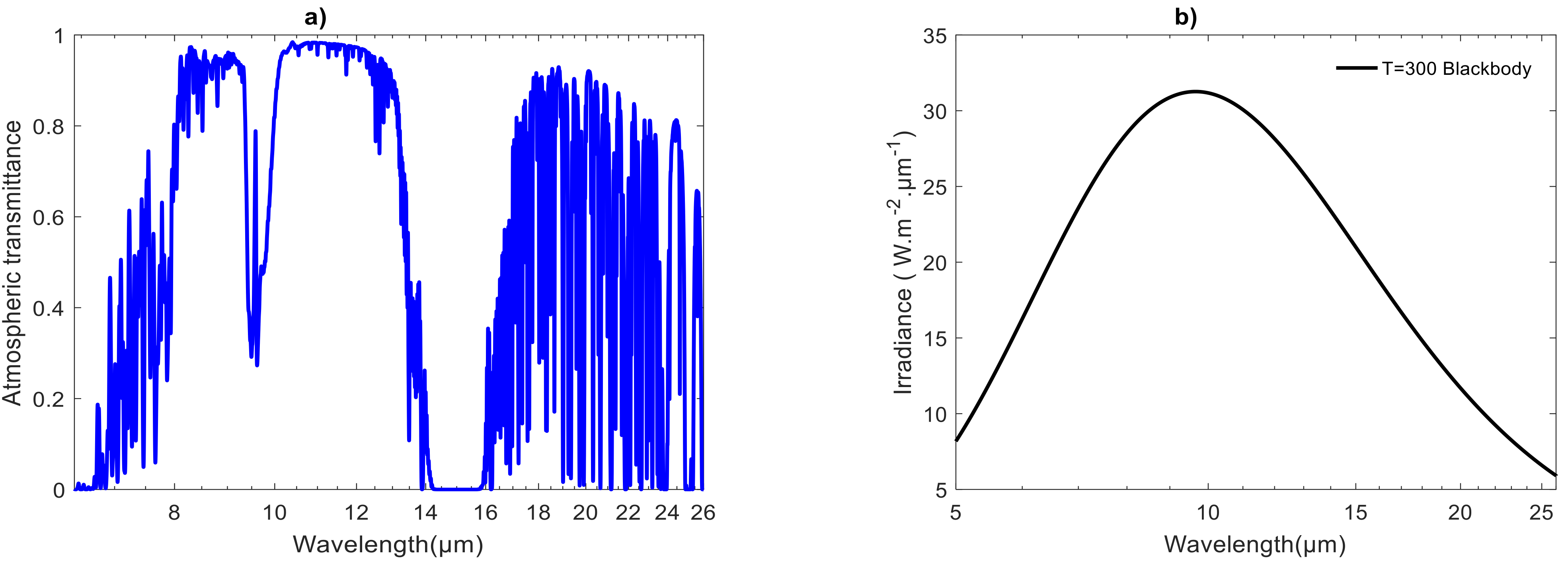 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Most of the terrestrial radiation is absorbed in the lower part of the troposphere. In the greenhouse effect shortwave solar radiation passes through the atmosphere. However since the Earth is much cooler than the Sun its radiating energy is much weaker long wavelength infrared energy. Greenhouse gases are molecules in the atmosphere that absorb long-wavelength infrared energy radiated by the Earth. A significant amount of radiation is also absorbed by the atmosphere a process called Atmospheric Absorption.
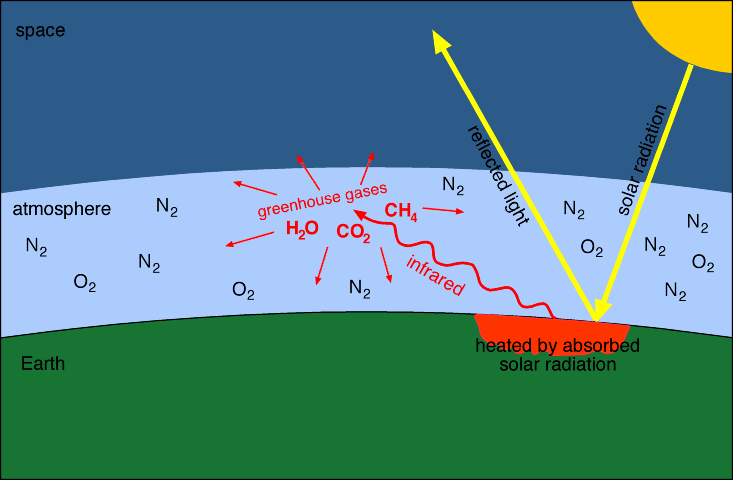 Source: columbia.edu
Source: columbia.edu
However since the Earth is much cooler than the Sun its radiating energy is much weaker long wavelength infrared energy. In the Earths climate system long-wave radiation involves processes of absorption scattering and emissions from atmospheric gases aerosols clouds and the surface. Most of the terrestrial radiation is absorbed in the lower part of the troposphere. This article examines what atmospheric absorption is how it occurs and what parts of solar radiation are affected. In the greenhouse effect shortwave solar radiation passes through the atmosphere.
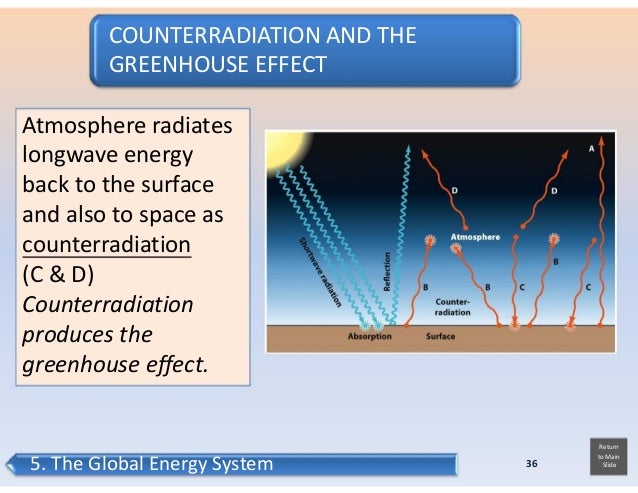 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Incoming and outgoing long-wavelength radiation is absorbed by water vapor carbon dioxide and other gases in the atmosphere. The ground then re-radiates that heat as outgoing long wavelength IR radiation F g. Longer wavelength than before it can get absorbed by the water vapour carbon dioxide methane and other greenhouse gases which are present in the atmosphere. Energy released from the Sun is emitted as shortwave light and ultraviolet energy. This article examines what atmospheric absorption is how it occurs and what parts of solar radiation are affected.
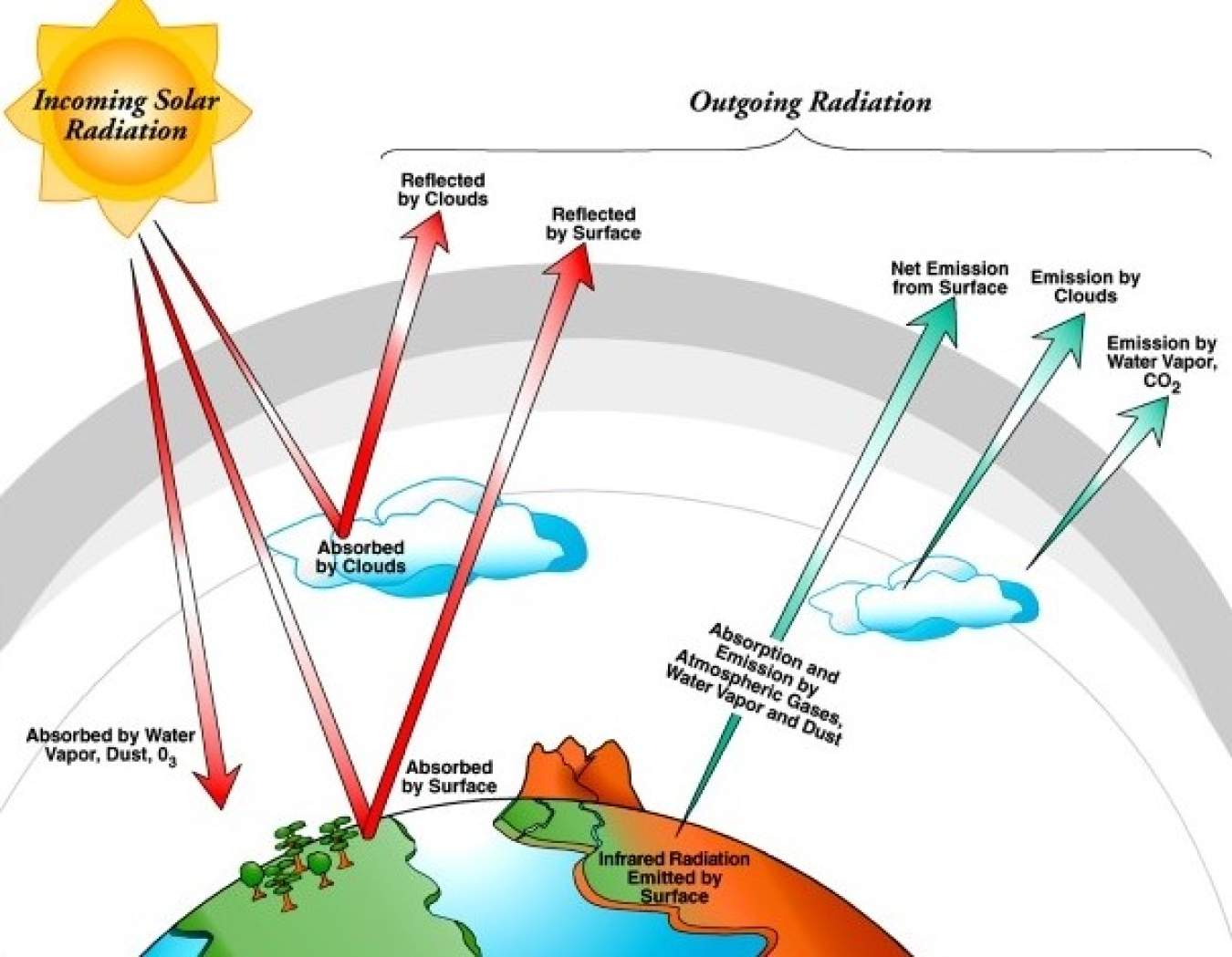 Source: energy.gov
Source: energy.gov
Energy released from the Sun is emitted as shortwave light and ultraviolet energy. Energy released from the Sun is emitted as shortwave light and ultraviolet energy. Longer wavelength than before it can get absorbed by the water vapour carbon dioxide methane and other greenhouse gases which are present in the atmosphere. Most of the terrestrial radiation is absorbed in the lower part of the troposphere. The heated layer can then radiate energy back to Earths surface.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
The atmosphere contains certain components most notably water molecules that absorb some wavelengths of outgoing longwave radiation OLR. This outgoing long wave radiation emitted by the earth surface is called terrestrial radiation. This energy is ultimately reradiated back into the atmosphere from the surface at a. The long wave radiation escapes to space in between 80µ and 130µ this is known as atmospheric window. A large portion of electromagnetic energy is scattered refracted diffused and reflected by the surface and atmosphere.

Some of this radiation is absorbed by the atmosphere directly but the majority is absorbed by the surface. Thus about 71 percent of the total incoming solar energy is absorbed by the Earth system. This article examines what atmospheric absorption is how it occurs and what parts of solar radiation are affected. This outgoing long wave radiation emitted by the earth surface is called terrestrial radiation. One of the most important factors is the greenhouse effect a simplified explanation of which is as follows Short-wave solar radiation can pass through the clear atmosphere relatively unimpeded But long-wave terrestrial radiation emitted by the warm surface of the Earth is partially absorbed and then re-emitted by a number of trace gases in the cooler atmosphere above Since on average the outgoing.
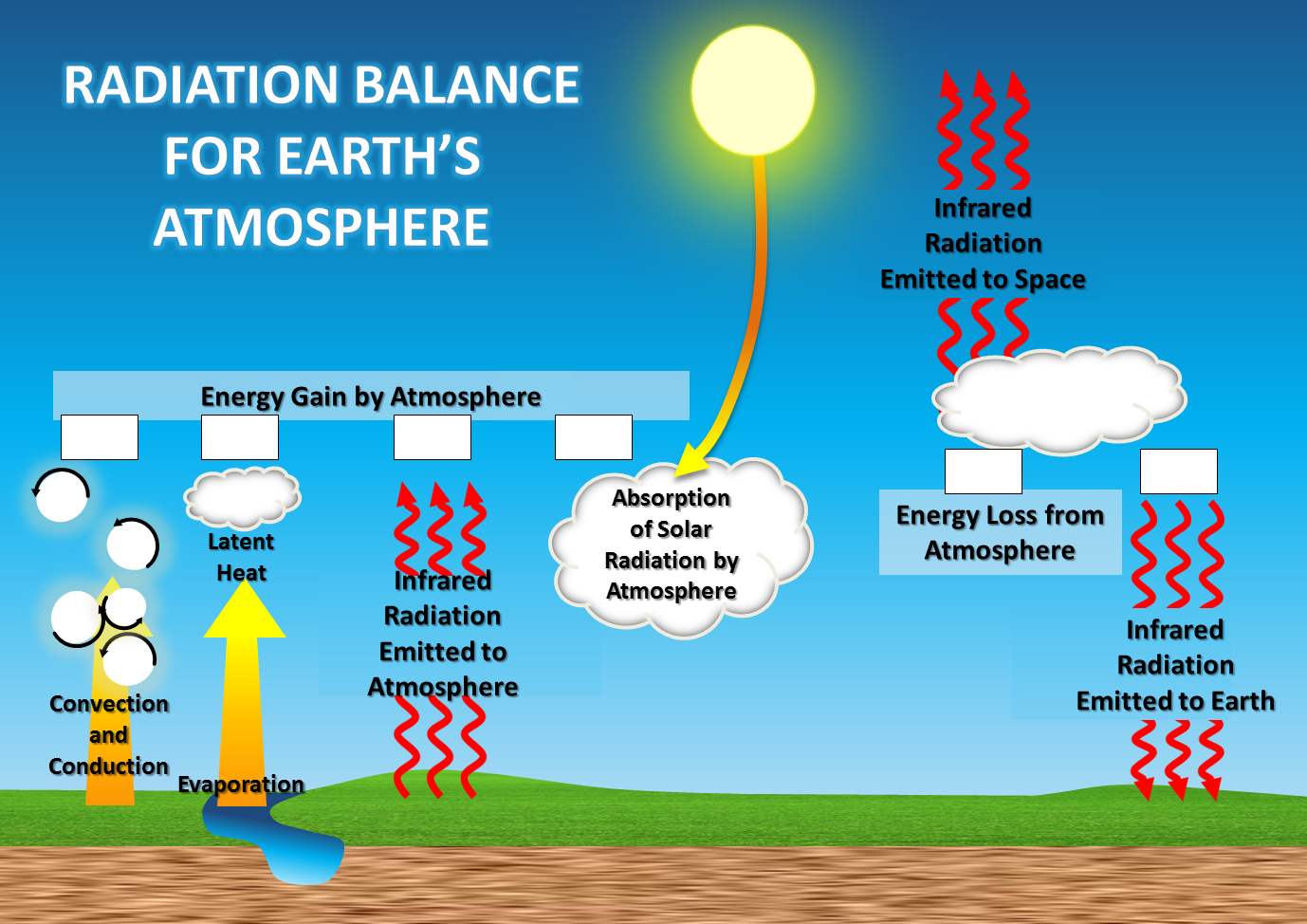 Source: ces.fau.edu
Source: ces.fau.edu
Some of this radiated energy will dissipate into space but a significant amount of heat will be absorbed by the atmosphere. Most of the terrestrial radiation is absorbed in the lower part of the troposphere. The dips in the incoming and outgoing energy are where the atmosphere absorbs energy. Some gases in the atmosphere can absorb Earths long-wave radiation and heat up the surrounding air by collisions with the neighboring molecules. Over 99 of outgoing long-wave radiation has wavelengths between 4 μm and 100 μm in the.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
When it reaches the Earth some is reflected back to space by clouds some is absorbed by the atmosphere and some is absorbed at the Earths surface. The heated layer can then radiate energy back to Earths surface. These molecules move more rapidly when. However since the Earth is much cooler than the Sun its radiating energy is much weaker long wavelength infrared energy. Incoming energy from the sun and outgoing energy from the earth relative to the electromagnetic spectrum.
 Source: energy.gov
Source: energy.gov
Thus about 71 percent of the total incoming solar energy is absorbed by the Earth system. The long wave radiation escapes to space in between 80µ and 130µ this is known as atmospheric window. Some of the incoming energy is absorbed by the atmosphere whereas most of the infrared energy emitted by the earth is absorbed. The atmosphere contains certain components most notably water molecules that absorb some wavelengths of outgoing longwave radiation OLR. Thus about 71 percent of the total incoming solar energy is absorbed by the Earth system.
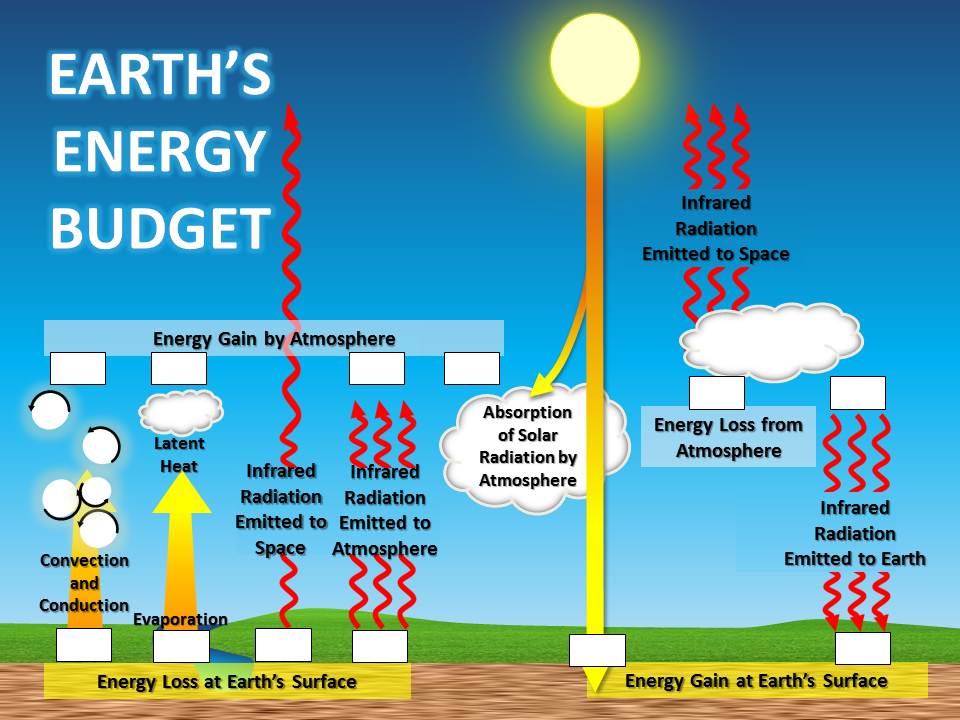 Source: ces.fau.edu
Source: ces.fau.edu
This energy plays no role in Earths climate system. The ground then re-radiates that heat as outgoing long wavelength IR radiation F g. This energy is ultimately reradiated back into the atmosphere from the surface at a. Exchange of Terrestrial Radiation. That flux is absorbed by the ground and the ground heats up to some temperature T g.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
As the water vapour methane carbon dioxide molecules absorb the longwave radiation they heat. About 23 percent of incoming solar energy is absorbed in the atmosphere by water vapor dust and ozone and 48 percent passes through the atmosphere and is absorbed by the surface. EM wavelength spectrum and examples of objects related to the different. When it reaches the Earth some is reflected back to space by clouds some is absorbed by the atmosphere and some is absorbed at the Earths surface. Some of the incoming energy is absorbed by the atmosphere whereas most of the infrared energy emitted by the earth is absorbed.
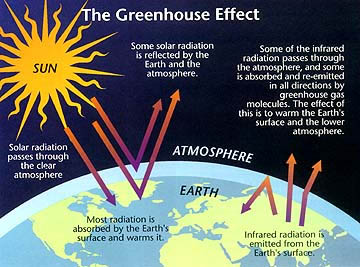 Source: soest.hawaii.edu
Source: soest.hawaii.edu
The energy associated with a single photon is given by E h ν where E is the energy SI units of J h is Plancks constant h 6626 x 10 34 J s and ν is the frequency of the radiation SI units of s 1 or Hertz Hz see figure below. In the greenhouse effect shortwave solar radiation passes through the atmosphere. This effect of trapping the outgoing long-wave Figure 1. Greenhouse gases are molecules in the atmosphere that absorb long-wavelength infrared energy radiated by the Earth. The long wave radiation escapes to space in between 80µ and 130µ this is known as atmospheric window.
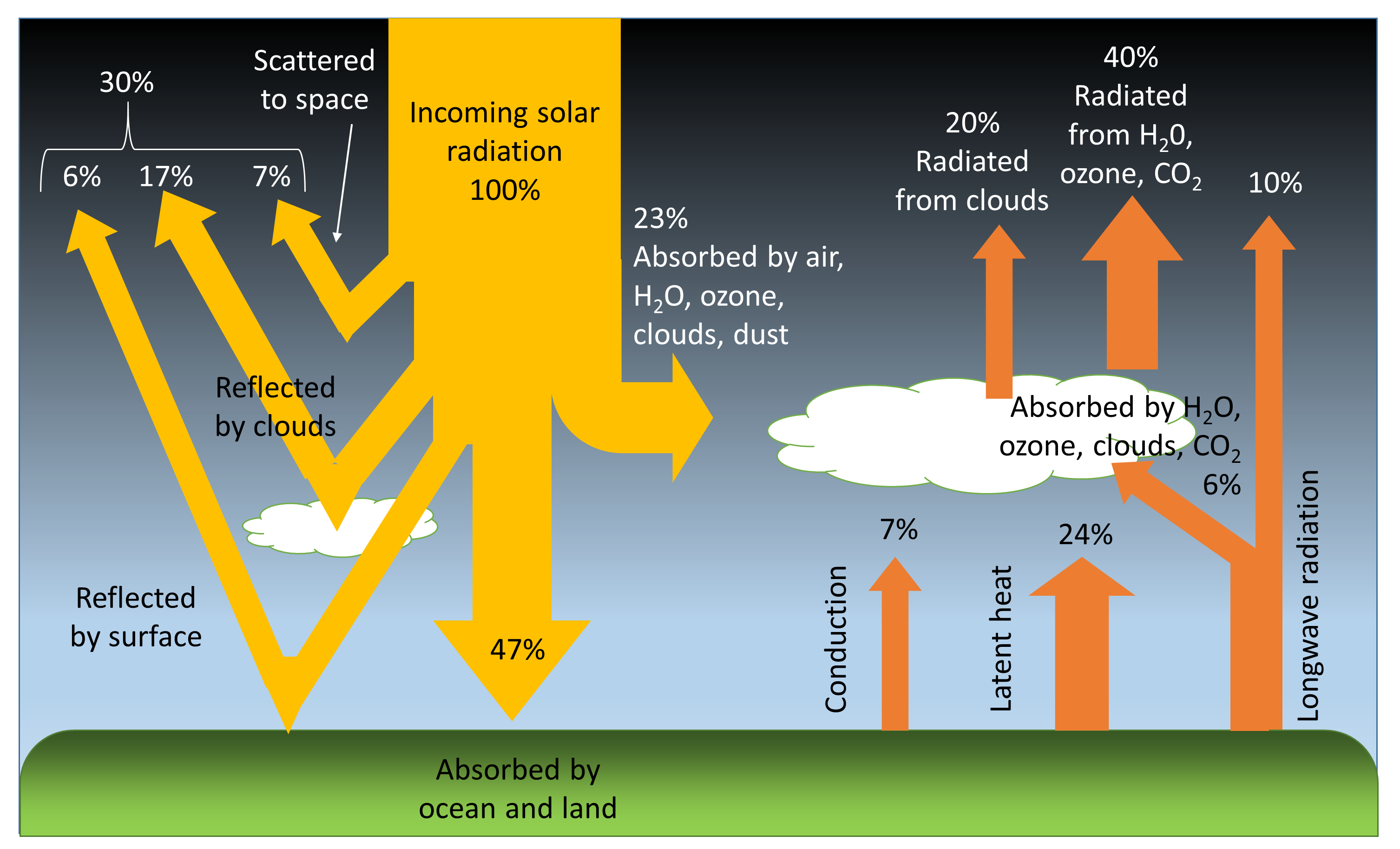 Source: rwu.pressbooks.pub
Source: rwu.pressbooks.pub
The atmosphere contains certain components most notably water molecules that absorb some wavelengths of outgoing longwave radiation OLR. This effect of trapping the outgoing long-wave Figure 1. Some of that flux F g is absorbed by the atmosphere through its long wavelength transmittance T t where 0 t t 10. Incoming and outgoing long-wavelength radiation is absorbed by water vapor carbon dioxide and other gases in the atmosphere. However since the Earth is much cooler than the Sun its radiating energy is much weaker long wavelength infrared energy.

This energy is ultimately reradiated back into the atmosphere from the surface at a. The long wave radiation escapes to space in between 80µ and 130µ this is known as atmospheric window. EM wavelength spectrum and examples of objects related to the different. The ground then re-radiates that heat as outgoing long wavelength IR radiation F g. This article examines what atmospheric absorption is how it occurs and what parts of solar radiation are affected.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title atmosphere but some of the outgoing long wavelength energy is absorbed and by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.